Cell and Tissue Related to Medical Technology _ Human Anatomy (1주차 - 2)
3. Tissues
- Four basic types of tissue :
(1) Epithelial tissue - cover and protect body structure and organs, vessels, cavities.
(2) Connective tissue - support and bind body structure(adipose, cartilage, blood)
(3) Muscule tissue - Contract to produce movement (skeletal, cardiac, etc)
(4) Nervous tissue - make up the brain, spinal cord and nerve (Neuron)
4. Protein Synthesis Process
- DNA Transcription is occur so mRNA is made in Nucleus.
- mRNA is move out from Nucleus through nuclear pore and it move to cytoplasm.
- mRNA is go into Ribosome that attached in ER, and mRNA that code with codon is combine with tRNA.
- tRNA call amino acid that code with codon and it make a polypeptide, and if they meet stop codon(UAA, UAG, UGA) the translation is stop.
- A polypeptide chain that made from number 4 often fold with 2 or 3 dimension structure. We call this process as protein folding, and it is generally necessary for protein’s function.
- 핵에서 DNA의 전사가 일어나 mRNA가 만들어진다.
- mRNA가 핵의 핵공을 통해 세포 밖으로 나오게 되고 세포질로 이동하게 된다.
- ER에 붙어있는 리보솜에 mRNA가 들어가고, mRNA에 맞는 코돈은 tRNA에 결합한다.
- 그에 맞는 아미노산을 불러오고 폴리펩타이드를 형성하며 정지코돈(UAA, UAG, UGA)을 만나면 멈추게 된다. 이를 번역과정이라고 한다.
- 만들어진 폴리펩타이드 사슬은 종종 2차 및 3차 구조로 접히게 된다. 이 과정을 단백질 접힘이라고 하며, 일반적으로 단백질의 기능에 필수이다.
5. DNA Replication
identical copies of DNA
double strand에서 base sharing을 자르고, 각각의 strand에 새로운 complimentary base sharing을 하는 나선이 붙는다.
수정란 1 Cell -> 수십조 cells
Cell divides (called mitosis)
DNA must be replicated so that each daughter cell has a copy
DNA replication involves several processes :
first, the DNA must be unwound, separating the two trands.
the single strands then act as templates (주형, 복제틀) for synthesis of the new strands, which are complimentary in sequence
bases are added one at a time until two new DNA strands that exactly duplicate (복제하다) the original DNA are produced.
semi conservative replication because one strand of each daughter DNA comes from the parents DNA and one strand is new. (한 가닥은 Parent strand, 한가닥은 new strand)
Hydrolysis of phosphate groups as the phosphodiester bonds form between the bases
- Enzymes & Proteins
Helicase : The enzyme unwinds several sections of parents DNA(DNA 찢어지는 곳에 위치함. 풀었을 때 Replication Fork라는 공백이 생긴다.)
SSBs(single strand binding proteins) stabilize strands, prevent annealing-> 모든 스트레인에 붙어있고, 싱글이 더블로 바뀌면 SSB는 날라간다.
Primase : create RNA primers, required to start replication(여기에서 복제가 시작된다, primer는 복제된 RNA, 시작되는 곳을 알려줌)
DNA polymerase : Binds at primers and builds from there, (make complimentary DNA ) -> It catalyzes the formation of 5’ - 3’ ester bonds of the leading strand.
(polymerase가 DNA를 건축함.)
Lagging strand which grows in the 3’-5’ direction is synthesized in short sections calld Okazaki fragments
Okazaki fragments : Primase + DNA polymerase
RNAse H (Enzyme): Remove RNA primer (important on lagging strand) -> DNA polymerase fills the gap
DNA ligase : The Okazaki fragments are joined. (to give a single 3’ - 5’ DNA strand)
- Process
First, Helicase unwinds DNA Double strand to Single strand
Second, SSBs are attached to each strand to prevent annealing
Third, SSBs are gone, and Primase attached to each strand.
Fourth, Primase creates RNA primers, required to start replication
Fifth, DNA polymerase binds at primer and builds grom there.
every new strand 들은 5‘->3’ 방향으로 생성된다. (Parent DNA strand 기준으로는 3에서 5번 carbon으로 생성된다.)
Leading strand : continuously
Lagging strand : discontinuously called semi - discontinuous
6. Trancsription
Transcription : DNA -> RNA(mRNA)
genetic messages are read and carried out of the cell nucleus to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs.
DNA : Template strand 라는 특정한 스트레인을 기준으로 다시 베이스 페어링이 일어남.

2번이 template strand일 때, 1번은 그 반대이고, mRNA는 1번에서 Thymine 대신 Uracil 이 들어가게 된다.
mRNA가 decode되면서 polypeptide 라는 단백질이 만들어지고, amino acid 가 모여서 만들어진다.
Transcription process
DNA double helix unwind, 따로 double strand가 된다.
mRNA가 template strand에 Base sharing을 이룬다. Ribonucleotides line up
Bonds form 5’ -> 3’(DNA), 3’-5’(RNA)**
U and T사이에 Replacement 일어남.**
initiation point -> TATA BOX sequence(TATAWAW, W -> A or T)부터, 그 부분이 시작점이다.
Regulation of Transcription
Transcription Factor : up -> activation(upstream enhance), down : Repressor
rate조절이 feedback control 을 통해 가능하다.
Temple strand(Antisence strand.)
RNA polymerase reads 3’ to 5’,
mRNA is built 5’ to 3,
mRNA is made of RNA (ribose sugar and U instead of T)
Termination을 통해 떨어져 나감. -> Terminator을 만나서 RNA가 바깥으로 나온다. Polymerase도 나오게 된다.
an mRNA is has been produced, and DNA is winding again.
만들어진 mRNA가 splicing 을 거치고 nucleus에서 나오게 된다.
Splicing
- Genes are made of exons and introns
- Introns have Non-necessary genetic cords.
- We call the initial mRNA called pre-RNA, and it include Introns. It must be processed before it can be read by the tRNA. (Ribosome 이 있는 tRNA)
- So, remove Introns from mRNA by processing (called splicing), and only Exons left in mRNA.
- While the mRNA is still in the nucleus, the introns are removed from the pre-RNA
- And mRNA is get out from the nucleus, it goes to the Cytoplasm
7. Translation
- Genetic cord
A group of three bases (a triplet) controls the production or a particular amino acid. (3개당 1개의 아미노산.)
process
(1) mRNA(reading frame) is get in to tRNA.
(2) tRNA brings anticodon, which is making a complementary base pairing with Codon. (and anticodon carried by a specific tRNA)
(3) Amino acids are attached to the tRNAs for each triplet.
For one amino acids, it has three bases, so 4*4*4 = 64 possibilities. (하나의 아미노산에는 베이스가 세 개 들어갈 수 있으니, 총 4의 3승인 64개의 가능성이 있다.)
Reading the Genetic code
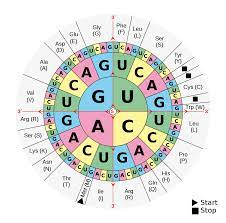
mRNA sequence
5’ -- CCU — AGC — GGA — CUU — 3’
라면,
CCU = Proline, AGC = Serine, GGA = Glycine, CUU = Leucine
일 때,
The mRNA section codes for the amino acid sequence of
Pro — Ser — Gly — Leu
Process of translation
AUG methionine (Start codon) -> 개시코돈으로, Translation 시작
UAA, UAG, UGA (Stop codon) -> Termination이 일어나면서 polypeptide 만들고 끝!
Termination
“stop” codon :There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop”codons.(안티코돈을 가진 tRNA가 없다.)
Therefore, protein synthesis ends.
polypeptide 가 모이면 3D가 된다.
some proteins begin folding while still being synthesized, others not fold up until after being released from the ribosome.
보통 termination 전까지는 folding 안한다. Termination 일어나면 리보솜 떨어져 나감. 그 이후 3D 형태로 folding 시작. 종종 termination전에도 folding 일어남.